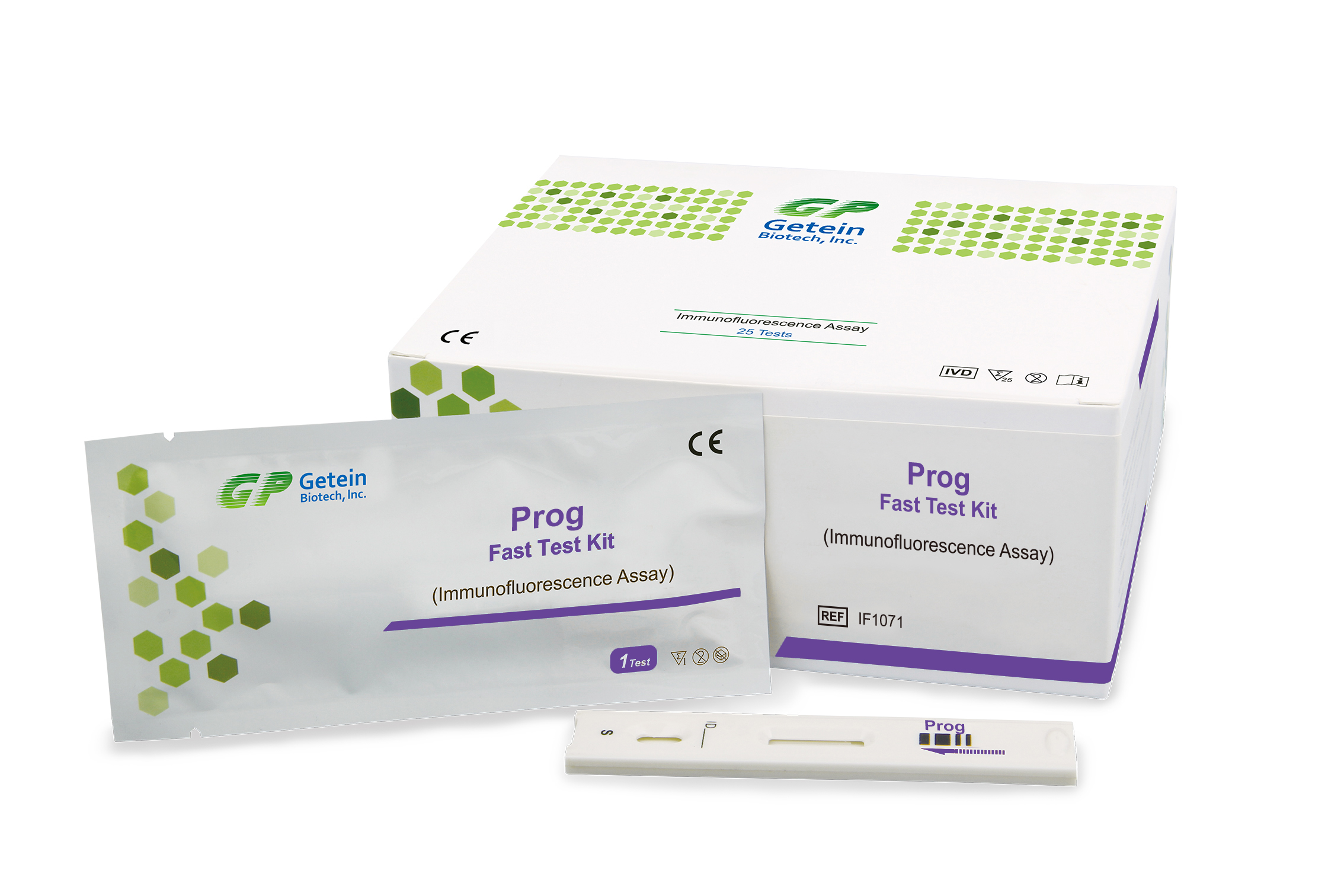
Description
Progesterone is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species.
Progesterone is produced by a woman’s ovaries throughout the process of releasing a mature egg from their ovary during ovulation and helps prepare the endometrium (uterine lining) to receive the egg in the event it is fertilized by a man’s sperm. However, if the mature egg goes unfertilized, levels of progesterone decrease, causing a woman to begin menstruation. If the woman does become pregnant, her placenta then begins to produce high levels of the hormone, beginning around the end of the first trimester and increasing until birth.
Progesterone tests are commonly used to determine the cause of infertility in female patients, as well as for monitoring the success of medications given to women to treat their infertility and treatments involving progesterone supplementation. They can also be utilized to determine if ovulation is occurring, to assess the possibility of miscarriage, monitor ovary and placenta functioning, and sometimes diagnose issues relating to the adrenal glands and some forms of cancer.