Description
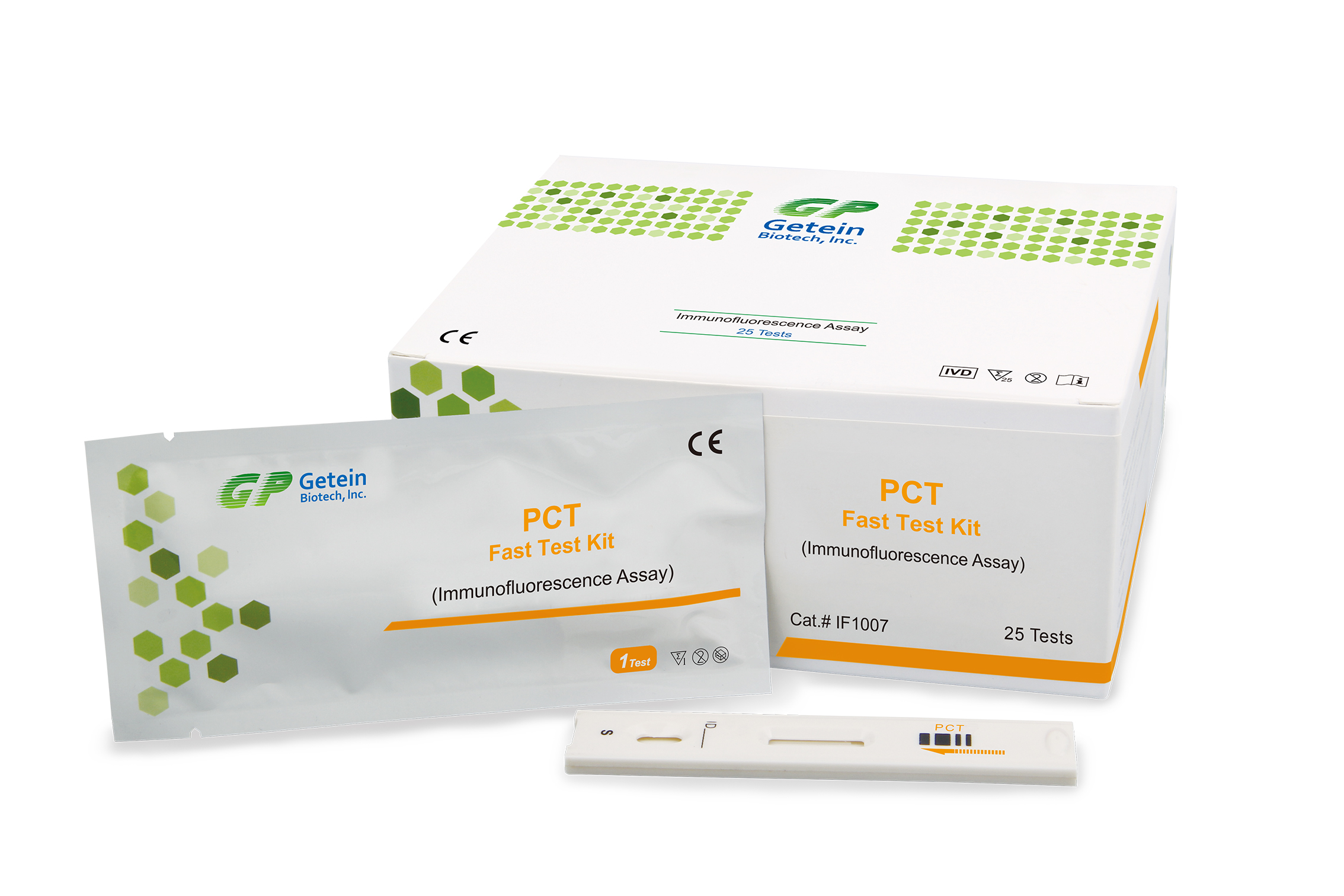
PCT is a peptide precursor of the hormone calcitonin, the latter being involved with calcium homeostasis. It is composed of 116 amino acids and is produced by parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid and by the neuroendocrine cells of the lung and the intestine.
Measurement of PCT can be used as a marker of severe sepsis and generally grades well with the degree of sepsis, although levels of PCT in the blood are very low. PCT has the greatest sensitivity and specificity for differentiating patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) from those with sepsis.
PCT levels may be useful to distinguish bacterial infections from nonbacterial infections. It has shown that PCT may help guide therapy and reduce antibiotic use, which can help save on cost of antibiotic prescriptions and drug resistance.