Description
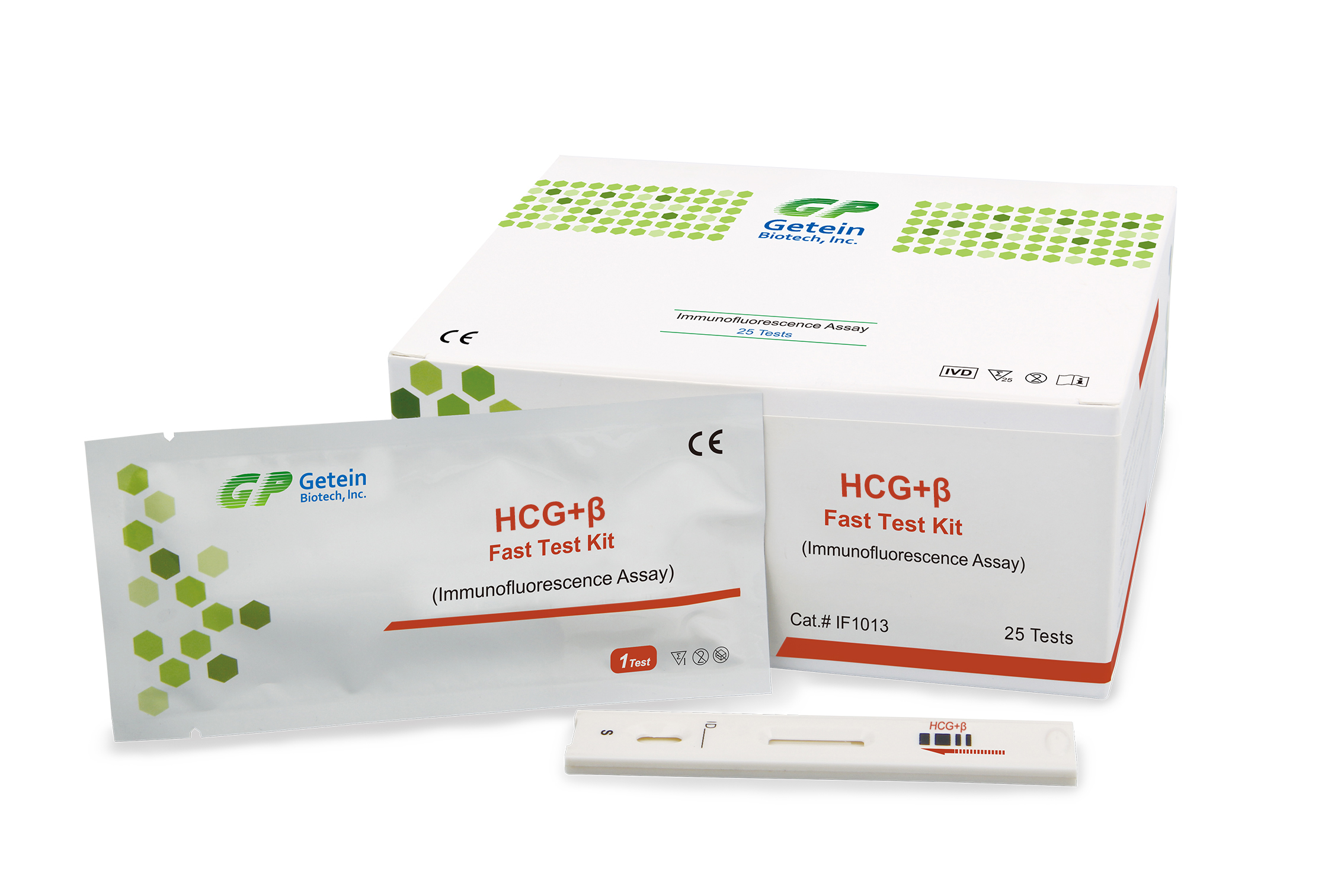
Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the placenta, a component of the fertilized egg, after conception. The biologically active hormone (intact HCG) is composed of noncovalently linked a and B subunit. The alpha subunit is similar to hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). whereas beta subunits is unique to HCG and confers its biological and immunological specificity. During a normal pregnancy, HG level can be detected soon after conception. It will double every 72 hours and reach its peak in the first 8~11 weeks of pregnancy.
HG measurement with blood or urine can be used as an aid in pregnancy test. Regular HCG has been known as a promoter of corpus luteal progesterone production, even though this function only explains 3 weeks of a full gestations production of regular HCG. HCG-positive indicates an implanted blastocyst and mammalian embryogenesis. Elevated values of HCG during pregnancy are indicative of chorionic carcinoma, hydatiform mole, or multiple pregnancy. HCG+ measurements can also be used in conjunction with other parameters during the second trimester of pregnancy to assess the risk of trisomy 21 (Down syndrome).