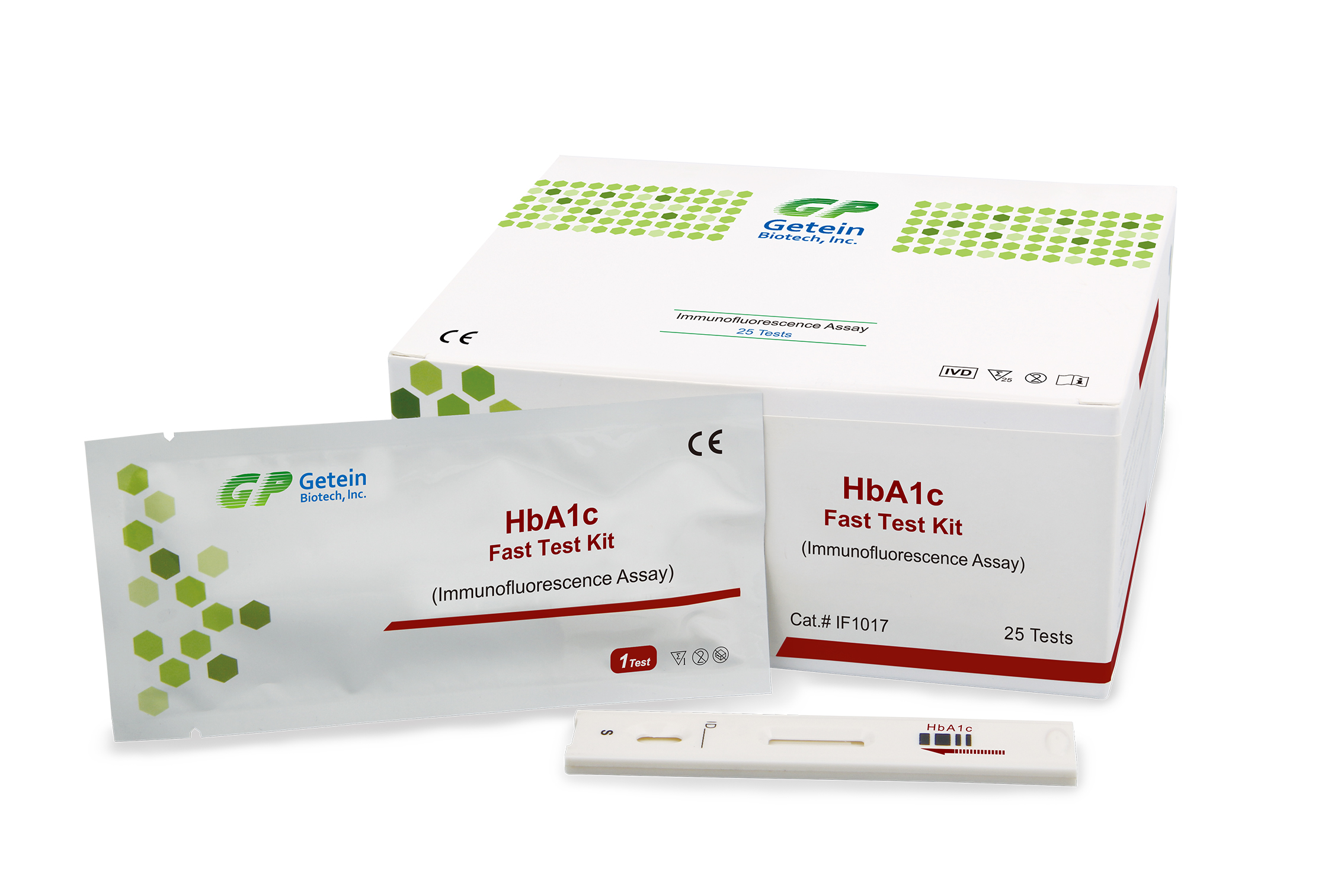
Description
Hemoglobin is the protein molecule in red blood cells with the main function transport oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood. HbA1c belongs to the glycated hemoglobin, a fraction formed by the attachment of various saccharides to the Hb molecule and is proportional to average blood glucose concentration over the previous four weeks to three months. One advantage of using HbA1c for diagnosis is that the test does not require a fasting blood sample. Although HbA1c testing is mainly used for monitoring blood sugar control in patients with diabetes, the World Health Organization (WHO) now recommends that HbA1c can be used as a diagnostic test for diabetes, provided that stringent quality assurance tests are in place and assays are standardised to criteria aligned to the international reference values.