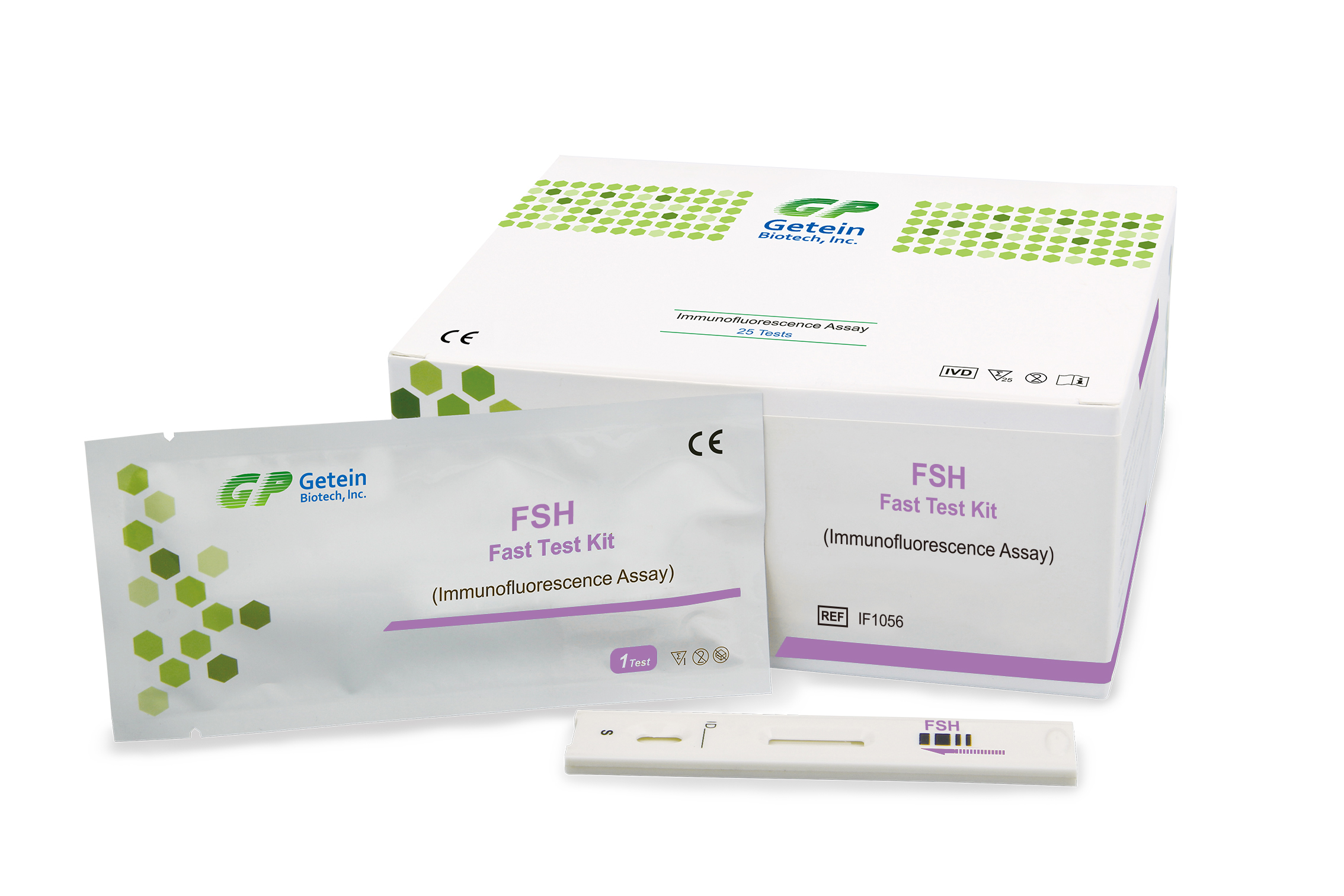
Description
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is one of the hormones essential to pubertal development and the function of women’s ovaries and men’s testes. Like other glycoproteins, such as LH, TSH and HCG, FSH consists of subunits designated as alpha and beta. Hormones of this type have alpha subunits that are very similarly structurally, therefore the biological and immunological properties of each are dependent on the unique beta subunit.
In women, this hormone stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles in the ovary before the release of an egg from one follicle at ovulation. FSH levels are elevated after menopause, castration and in premature ovarian failure. In men, FSH stimulates seminiferous tubule testicular growth, and is involved in the early stages of spermatogenesis. Oligospermic males usually have elevated FSH levels. High levels of FSH in men may be found in primary testicular failure and Kinefelter synd-rome. Elevated concentrations are also present in cases of starvation, renal failure, hyperthyroidism and cirrhosis.
It is a useful marker in the study of pituitary disease, classification of pituitary tumors and in the differential diagnosis of primary and metastatic tumors of the pituitary.